The study will assess the impact on quality of care after implementation of the ERAS
(Enhanced Recovery After Surgery) protocol for laparoscopic colorectal surgery in Vilnius
University Hospital Santaros klinikos. The primary goal of this study is to compare efficacy
of two different types of anaesthesia – general and combined (spinal and general), efficacy
of multimodal analgesia in both groups, need for rescue analgetics, time to bowel movement,
time to ambulation. We also aim to study overall patient satisfaction and measure
health-related quality of life, from date of randomisation until the date of hospital
discharge, 30 days, 3 months and 6 months post-discharge.
Clinical Trial – Use of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for the Treatment of Crush Injuries
The purpose of this study is to determine whether using hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) improves
wound healing for patients who have a crush injury. The comparison of the prospective
intervention group to the retrospective matched cohort aims to show that HBO can improve
wound healing and decrease poor outcomes for patients with crush injuries. The information
gained from this small study will serve as a basis for a follow-up prospective, randomized
control trial to further delineate the role of HBO in a larger patient population.
Retrospective Case Series of Traumatic Brain Injury and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Treated with Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
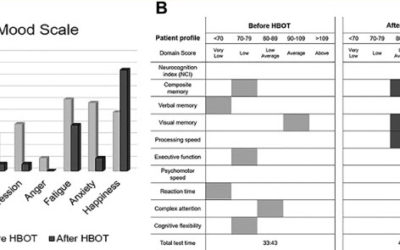
Returning veterans are frequently diagnosed with traumatic brain injury (TBI) and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Considering a recent case-controlled study of hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) reporting a reduction in suicidal ideation, we investigated retrospectively three veterans with chronic TBI/PTSD symptoms who were treated with multiple rounds of HBOT with neurophysiological testing performed before and after treatment. Improvements were detected on parameters within neurocognitive domains, including reductions in suicide-related symptoms. These findings independently confirm that HBOT may be effective in treating specific symptoms of TBI/PTSD that are not currently addressed with existing therapeutic approaches.
Clinical Trial – Hyperbaric Oxygen for Carbon Monoxide Induced Chronic Encephalopathy
in some patients, a few days or weeks after they recover from carbon monoxide poisoning they
develop new symptoms. These can affect mood, ability to think or remember clearly, and
movements. Some people develop movement problems that are similar to Parkinson’s disease.
This damage to brain tissue is called "encephalopathy," and this study will look at the
effect of pressurized oxygen therapy on long term, or chronic, encephalopathy.
Clinical Trial – Plethysmographic Variability Index in Post Spinal Anesthesia Hypotension in Cesarean Section
– Full term pregnant female patients presented for elective C.S for single viable fetus
will be included in this study.
– Before anesthesia, the patient will be attached to a monitor of: ECG , heart rate, non
invasive blood pressure, pulse taximeter applied on the index finger of the limb not
attached to the blood pressure cuff, pulse oximetry and plethysmographic variability
index (PVI) and perfusion index (PI) will be taken by (Massimo radical 7, Massimo corp.
USA). Measures will be recorded every 5 minutes preoperative.
– Patients with PVI <15 will be excluded from the study.
- Patients with PVI > 15 are started on intravenous infusion of warm ringer lactate
solution via suitable pore intravenous cannula to reach target of PVI <15 or a total 1
liter of ringer lactate.
- The patients in which the PVI is corrected by fluid to level below 15 will be Group (C)
or corrected group. Patients in which intravenous fluid administration did not result
any change in PVI or changed but still higher than 15 will be Group (NC) or non
corrected group.
After preoperative preparation patient is shifted to operating theater, with all monitors
applied. She will receive spinal block at lumbar 3-4 space with hyperbaric bupivacaine 8 mg
plus 25 mic fentanyl. After giving anesthesia and positioning for surgery with a left lateral
tilt of 15 degrees,
Clinical Trial – Erector Spinae Plane Block for Postoperative Pain Control in Hip Replacement Surgeries
ESP block advantages include its simplicity, easy identifiable ultrasonographic landmarks and
low risk for serious complications as injection is into tissue plane that is distant from
pleura, major blood vessels and discrete nerves. Coupled with the fact that the erector
spinae muscle and ESP extend down to the lumbar spine, ESP block was hypothesized to be
performed at the level of L4. In a recent case report, ultrasound guided ESP block was
successfully performed at L4 transverse process level for postoperative analgesia after total
hip arthroplasty. However, confirmation of the efficacy of ESP block in hip replacement
surgeries needed more investigation.
Clinical Trial – Quadratus Lumborum Block Versus Fascia Iliaca Block for Hip Arthroplasty
Quadratus lumborum block is a newly developed block with good performance in lower abdominal
surgery. In a cadaveric study, the spread of local anesthetic in the anterior approach of QL
block (QL3) was reported to cover nerve roots from T10 to L3. Thus, it was hypothesized that
this approach could be used in hip surgeries with minimal motor affection.
This study aims to compare QL3 block and suprainguinal Fascia Iliaca block in the duration of
postoperative analgesia, pain scores, motor power in quadriceps muscle, and side effects.
Treatment of Traumatic Brain Injury With Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) is defined as the use of oxygen at higher than atmospheric pressure for the treatment of underlying disease processes and the diseases they produce. Modern HBOT in which 100% O2 is breathed in a pressurized chamber dates back to the 1930s, when it was first used for treatment of decompression illness in divers. There are currently 13 FDA-approved uses for HBOT, including decompression illness, gas gangrene, air embolism, osteomyelitis, radiation necrosis, and the most recent addition—diabetic ulcers. HBOT can dramatically and permanently improve symptoms of chronic TBI months or even many years after the original head injury. This assertion is generally met with skepticism within the medical establishment because we have been taught for generations that any post-concussion symptoms persisting more than 6 months or so after a head injury are due to permanent brain damage that cannot be repaired.
Clinical Trial – Comparison of Clorotekal and Bupivacaine for Short Obstetric Surgery
The following obstetric procedures are commonly performed with spinal anesthesia on labor and
delivery: bilateral tubal ligation, external cephalic version, cerclage insertion, cerclage
removal, minimally invasive fetal surgery, and evacuation of retained products of conception.
Bupivacaine is currently the standard spinal medication for these procedures because of its
long history of safe use, its low incidence of transient neurologic symptoms, and its ability
to provide a dependable, dense block with a high degree of maternal satisfaction. While
bupivacaine has the aforementioned advantages, it unfortunately has a long duration of
action, up to 240-380 minutes, which far exceeds the time necessary to complete most
obstetric procedures. Clorotekal®, the first Food and Drug Administration approved
chloroprocaine solution created for spinal injection, is a potential alternative. When
compared with bupivacaine spinals, chloroprocaine spinals have been shown to facilitate
clinically significant shorter times to resolution of motor and sensory block, first
ambulation, micturition, and discharge readiness. The objective of this study is to determine
if a strategy of spinal anesthesia with chloroprocaine will reduce the duration of motor
block, compared with equivalent block with hyperbaric bupivacaine..
Clinical Trial – High-flow Oxygen for Vaso-occlusive Pain Crisis
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is characterized by recurrent vaso-occlusive pain crisis (VOC),
which may evolve to acute chest syndrome (ACS), the most common cause of death among adult
patients with SCD. Currently, there is no safe and effective treatment to abort VOC or
prevent secondary ACS. Management of VOC mostly involve a symptomatic approach including
hydration, analgesics, transfusion, and incentive spirometry, which was investigated in a
very limited number of patients (<30).
The polymerisation of HbS is one major feature in the pathogenesis of vaso-occlusion. Among
factors determining the rate and extent of HbS polymer formation, the hypoxic stimulus is one
of the most potent and readily alterable. Current guidelines recommend oxygen therapy in
patients with VOC in order to maintain a target oxygen saturation of 95%. Low-flow nasal
oxygen (LFNO) is routinely used to achieve this normoxia approach, particularly in patients
at risk of secondary ACS because they may experience acute desaturation. In contrast, various
case series suggest a potential beneficial role of intensified oxygen therapy targeting
hyperoxia for the management of VOC, particularly with the use of hyperbaric oxygen, but the
latter is difficult to implement in routine clinical practice.
A recent high-flow nasal oxygen (HFNO) technology allows the delivery of humidified gas at
high fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO2) through nasal cannula. The FiO2 can be adjusted up to
100% (allowing hyperoxia that may reverse sickling) and the flow can be increased up to 60
L/min (which generates positive airway pressure and dead space flushing, that may prevent
evolution of VOC towards ACS by alleviating atelectasis and opioid-induced hypercapnia). In
patients with acute respiratory failure, HFNO has been shown to improve patient's comfort,
oxygenation, and survival as compared to standard oxygen or non-invasive ventilation.
The aim of the present study is to test the efficacy and safety of HFNO for the management of
VOC and prevention of secondary ACS. The investigators will use a multi-arm multi-stage
(MAMS) design to achieve these goals. HFNO will be delivered through AIRVO 2 (Fisher and
Paykel Healthcare, New Zealand), a device that incorporates a turbine allowing its use in
hospital wards.